Introduction:
Amazon, founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994, has revolutionized the retail industry in ways unimaginable. From its humble beginnings as an online bookstore, Amazon has grown into a global e-commerce giant, dominating various sectors and redefining the way people shop, live, and work. With a market value of over $1 trillion, Amazon is not only the largest online retailer but also a leader in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and digital media.
Significant Impact on the Retail Industry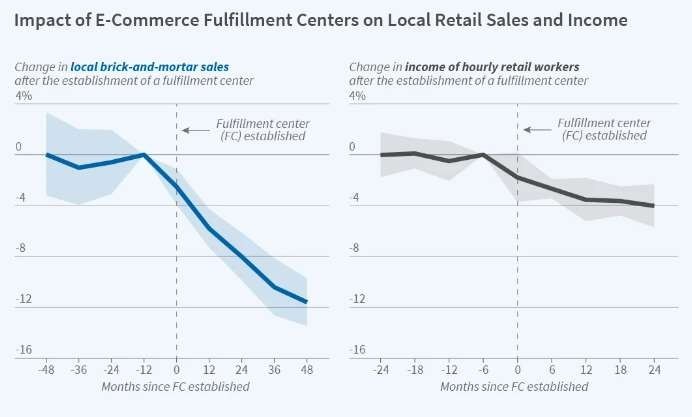
Amazon ‘s impact on the retail industry hour angle be profound . The company ‘s grim focus on customer satisfaction , vast merchandise choice , and innovative logistics hour angle coerce traditional retailer to reconsideration their business model . The rise of e-commerce , light- emitting diode by amazon , hour angle result in a significant shift in consumer behaviour , with more people turn to on-line shopping for convenience , competitive pricking , and personalized experience .
Key Statistics:
Amazon history for nearly 50 % of all e-commerce gross sales in the unite state . The company hour angle over 300 million active customer worldwide . amazon ‘s market value be larger than the combined market value of Palmar , target , and Osteo .
The amazon consequence :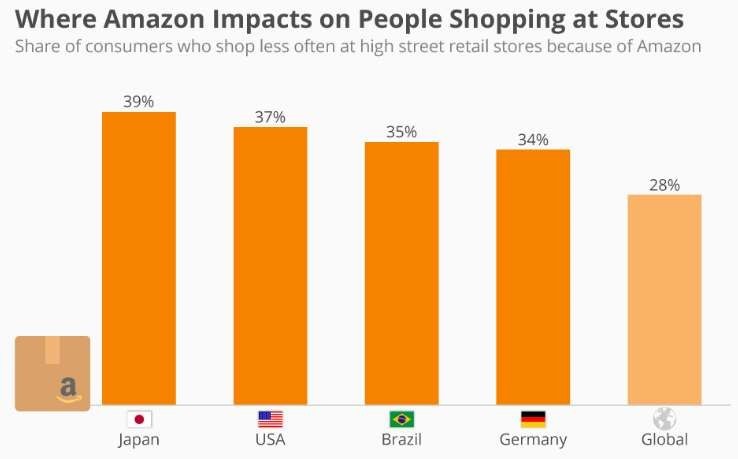
The amazon consequence mention to the profound impact the company hour angle have on the retail industry , coerce traditional retailer to adapt to a new era of e-commerce.
This includes:
Omnichannel Retailing :
Integration on-line and office channels to supply a fearless shopping experience . fast and free transportation : offer fast and free transportation option to stay competitive .
Innovative Logistics:
Investing in advanced logistics and supply chain management to reduce delivery times and costs.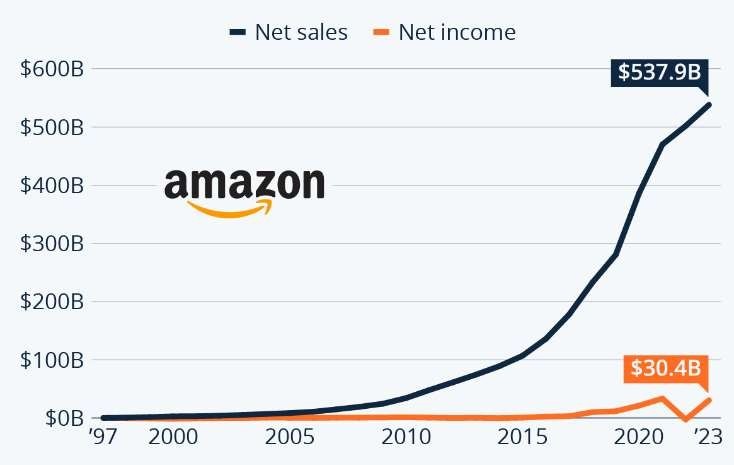
Business Model & Strategy:
Analyz amazon ‘s business model , include its key gross stream, customer central approach , and emphasis on convenience .
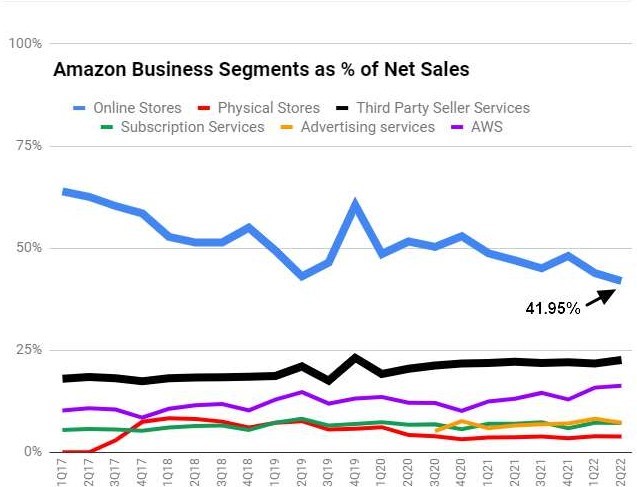
Graph: Breakdown of Amazon’s revenue streams (e.g., e commerce, AWS, subscriptions).
The company’s business model allowed it to offer products, starting with books, at lower prices than traditional brick-and-mortar stores. This competitive pricing strategy attracted more customers, which in turn increased the volume of sales, creating a cycle that fueled Amazon’s rapid growth.
Customer Personalization:
From personalized recommendations to Alexa's voice-activated shopping, Amazon uses data analytics and machine learning to anticipate customer needs and preferences. These strategies showcase Amazon's desire to place the customer right at the center of its business model.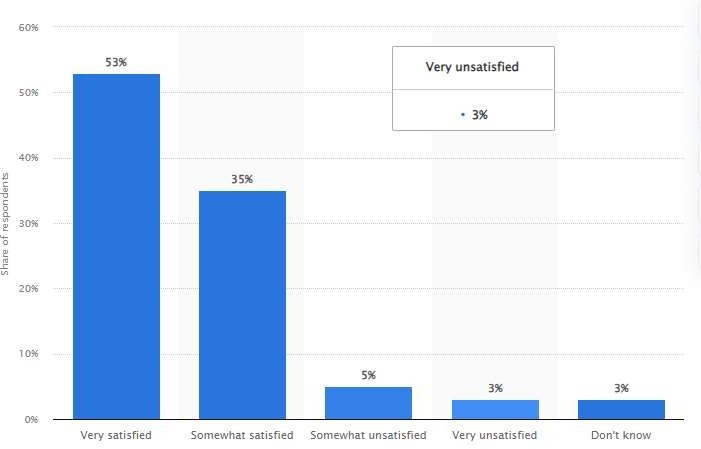
Amazon has leveraged data analytics to improve customer experience and drive business growth in several ways. They have invested substantially in customer analytics, using unconventional data sources and tools to analyze customer data and enhance customer centricity
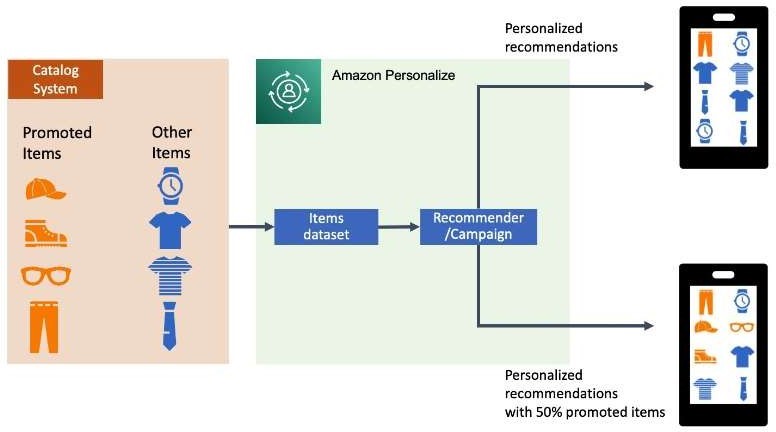
Marketplace & Sellers:
Third-party sellers are . independent seller who offer a variety of new, used, and refurbished items. The steps to place an order with a third-party seller are the same as placing any other order on Amazon.com. You add items to your cart and complete your order through the Amazon checkout process.
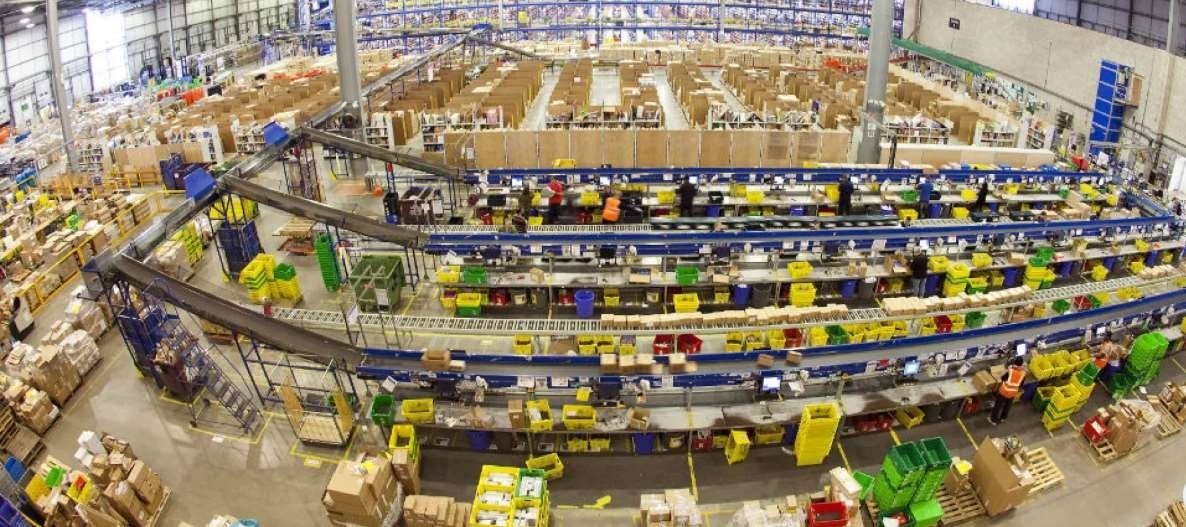
Logistics & Supply Chain:
Amazon’s supply chain management relies heavily on technology and is often among the first to integrate new technologies. The company uses robots, automated conveyor belts, and other technology in its fulfillment centers to streamline the process of sorting, storing, and shipping orders.

Technological Innovation:
Amazon has led the way on many technological fronts, from Cloud computing to e-readers, online grocery shopping, video streaming, and gaming.. Most are, not incidentally, ways to receive, consume, and store information, entertainment, and products that are sold by Amazon.
Expansion & Diversification:
Amazon has been able to meet the demands of online shoppers, providing them with an extensive selection of products across various categories. Amazon’s expansion strategies have been instrumental in its global success.
Technology & Innovation:
Amazon uses data analysis to analyse customer data, such as purchase history, browsing behaviour, and customer feedback, to identify common issues and proactively address them. Amazon also uses data to personalize the customer experience by providing tailored product recommendations, promotions, and offers.
CSR & Community:
Amazon prioritizes the use of sustainable packaging and has set ambitious goals to minimize waste and promote recycling. The company has invested in renewable energy projects to power its operations and has committed to achieving net zero carbon emissions across its entire business by 2040. Additionally, Amazon is actively engaged in community engagement efforts through partnerships with local organizations and initiatives that support small businesses.
Challenges & Outlook:
Amazon face several challenge in its corporate social duty and sustainability enterprise , include :
Lack of transparent in coverage carbon emission , with a evaluation of “ degree Fahrenheit ” class by wire magazine inconsistent committedness to climate pledge , such as silently remove its cargo nothing committedness increase emission , with a 40 % addition since 2019 , despite announce the climate pledge regulation examination , competition , and ethical concern , which can impact its ability to achieve its sustainability goal employee trust issue , with employee career for more action on climate change and knock the company ‘s lack of advancement
Conclusion:
Amazon’s innovative business model has revolutionized the e-commerce industry, transforming the way people shop, and setting a new standard for customer experience.
Beyond e-commerce, Amazon’s impact extends to cloud computing, artificial intelligence, robotics, and more, making it a leader in multiple industries.
Amazon’s focus on customer obsession, innovation, and long-term thinking has enabled it to disrupt traditional industries and create new markets. Lessons Learned from Amazon’s Business Model
Customer Obsession: Amazon’s relentless focus on customer satisfaction has led to its success. Other businesses can learn from Amazon’s customer-centric approach and prioritize customer needs.
Innovation and Experimentation: Amazon’s willingness to experiment and invest in new technologies has enabled it to stay ahead of the competition. Other businesses can adopt a similar approach to drive innovation.
Long-term Thinking: Amazon’s focus on long-term growth and sustainability has allowed it to make bold bets and investments. Other businesses can learn from Amazon’s patience and commitment to long-term success.
Diversification and Expansion: Amazon’s expansion into new markets and industries has enabled it to reduce dependence on a single revenue stream. Other businesses can explore diversification opportunities to drive growth.
Emphasize Customer Experience: Non-technical businesses can focus on delivering exceptional customer experiences, leveraging technology to enhance customer interactions.
Invest in Innovation: Non-technical businesses can invest in innovation and R&D to stay competitive, even if they don’t have a technical background.