McDonald's Case Study

Introduction:
McDonald’s Corporation, founded in 1940 as a café by Richard and Maurice McDonald in San Bernardino, California, USA, initially operated as a burger stand. Later, they revamped their business model, evolving it into a franchise, with the iconic Golden Arches logo introduced in 1953 at a location in Phoenix, Arizona.
McDonald’s, previously headquartered in Oak Brook, Illinois, relocated its global headquarters to Chicago in mid-2018.
McDonald’s restaurants are present in 120 countries and territories globally, serving approximately 68 million customers daily. With a total of 37,855 restaurants worldwide, McDonald’s employs over 210,000 people as of the end of 2018.
While McDonald’s is renowned for its burgers, cheeseburgers, and French fries, its menu extends to include chicken items, breakfast selections, beverages like sodas and milkshakes, wraps, and desserts. Responding to shifting consumer preferences and criticism regarding the nutritional value of its food, the company has incorporated salads, fish, smoothies, and fruits into its offerings.
McDonald’s Corporation generates revenue from leases and fees paid by its franchisees. As per two reports released in 2018, McDonald’s ranks as the world’s second-largest private employer, with 1.7 million employees, trailing only behind Walmart, which employs 2.3 million workers.
McDonald’s Company Highlights
COMPANY NAME | MCDONALD’S |
Headquarters | Chicago, Illinois , U.S. |
Founded | 1940 |
Founders | Richard and Maurice McDonald’s and then by Ray Kroc |
Sector | Restaurants, Food Franchise, Real Estate |
Valuation | $185+ bn |
Revenue | $23.22 bn (FY21) |
McDonald’s – Startup Story and History
In 1940, Richard and Maurice McDonald launched the original McDonald’s restaurant at 1398 North E Street at West 14th Street in San Bernardino, California. However, the McDonald’s of that time was quite different from the familiar chain we know today. It was Ray Kroc who made significant alterations to the brothers’ business model, transforming and modernizing it into the McDonald’s brand recognized worldwide.
In 1948, the McDonald brothers introduced the “Speeded Service System,” which expanded on the principles of the modern drive-thru restaurant, first tested by White Castle over two decades earlier. McDonald’s revolutionized the dining experience with a delivery model that utilized a conveyor belt to prepare and deliver food within a remarkable 2-minute timeframe.
This innovative approach created an extraordinary and unprecedented restaurant concept featuring:
- A limited menu offering only burgers, fries, and shakes
- Elimination of plates and wait staff, providing a streamlined and efficient service experience for customers.
As McDonald’s expanded its presence into numerous international markets, it became synonymous with globalization and the American way of life. However, its prominence has also made it a frequent subject of public debates concerning issues such as obesity, corporate ethics, and consumer responsibility.
McDonald’s – Mascot/Logo
Initially, McDonald’s first mascot was “Speedee,” depicted as a cooking cap atop a burger. However, in 1962, the Golden Arches symbol replaced Speedee as the company’s universal mascot. The iconic character of Ronald McDonald, a clown, was introduced in 1965 to engage with children and promote the brand.

On May 4, 1961, McDonald’s filed its first U.S. trademark application for the name “McDonald’s,” specifying “Drive-In Restaurant Services.” Subsequently, on September 13, under the guidance of Ray Kroc, McDonald’s filed another trademark application for a new logo— covering, twofold curved “M” image..

Products
McDonald’s primarily offers hamburgers, a variety of chicken options, chicken sandwiches, French fries, breakfast items, and desserts. In most locations, they also provide salads and vegetarian choices, wraps, and other menu items tailored to local preferences. Additionally, the seasonal McRib sandwich adds excitement to the menu for some customers. Meals are available for either dining in or take-out, with dine-in orders served on plastic trays with paper inserts and take-out orders packaged in the distinctive brown paper bags branded with the McDonald’s logo.
Under CEO Steve Easterbrook’s leadership, McDonald’s has simplified its menu, reducing the number of items from nearly 200 in the United States. The company has also focused on introducing healthier options, such as eliminating high-fructose corn syrup from hamburger buns and removing artificial preservatives from Chicken McNuggets. Artificial preservatives, flavors, and colors have been entirely eliminated from seven classic burgers in the U.S. as of September 2018, although pickles still contain an artificial preservative, though customers can request their burgers without pickles.
McDonald’s restaurants in various countries, especially in Asia, offer local deviations from the standard menu, catering to regional food preferences or cultural norms. For instance, in India, where beef consumption is prohibited for religious reasons, alternative menu items are available. Similarly, McDonald’s offers items like McRice in Indonesia and prawn burgers in Singapore and Japan to cater to local tastes. In some Western European countries, including Germany, McDonald’s also sells beer. In New Zealand, McDonald’s sells meat pies, following the partial relaunch of the Georgie Pie fast food chain, which McDonald’s acquired in 1996.
McDonald’s – Business Model And Market Strategy
Operating in over 100 countries with close to 40,000 restaurants worldwide, McDonald’s business model depends mainly on franchisees to sell its products, often leasing properties owned by the company. Originally this business model was first adopted by brothers Richard James and Maurice James McDonald, who later sold their enterprise to Ray Kroc, their initial franchise agent, for a significant sum of US$ 2.7 million in 1961.
In 2021, McDonald’s solidified its position as the most valuable Quick Service Restaurant (QSR) brand by prioritizing its business model focused on providing fast service and delivering consistently high-quality products. This approach led to a brand value of US$ 154.9 billion and global revenue of US$ 19.21 billion, reaffirming McDonald’s dominance in the industry.
McDonald’s owes much of its current success to its effective marketing strategy. Since its early expansion, the company prioritized establishing robust brand recognition and widespread market presence to support its growing franchise network. With an increasing customer base, McDonald’s conducted extensive demographic research to better target its audience. Their marketing approach involves investing in both online and offline channels to disseminate clear, brand-focused messages to a wide audience. Additionally, they utilize platforms like their dedicated mobile app to engage and retain loyal customers.
Presently, McDonald’s holds the title of the world’s largest restaurant chain based on revenue.
McDonald’s VISION, MISSION AND CORE VALUES
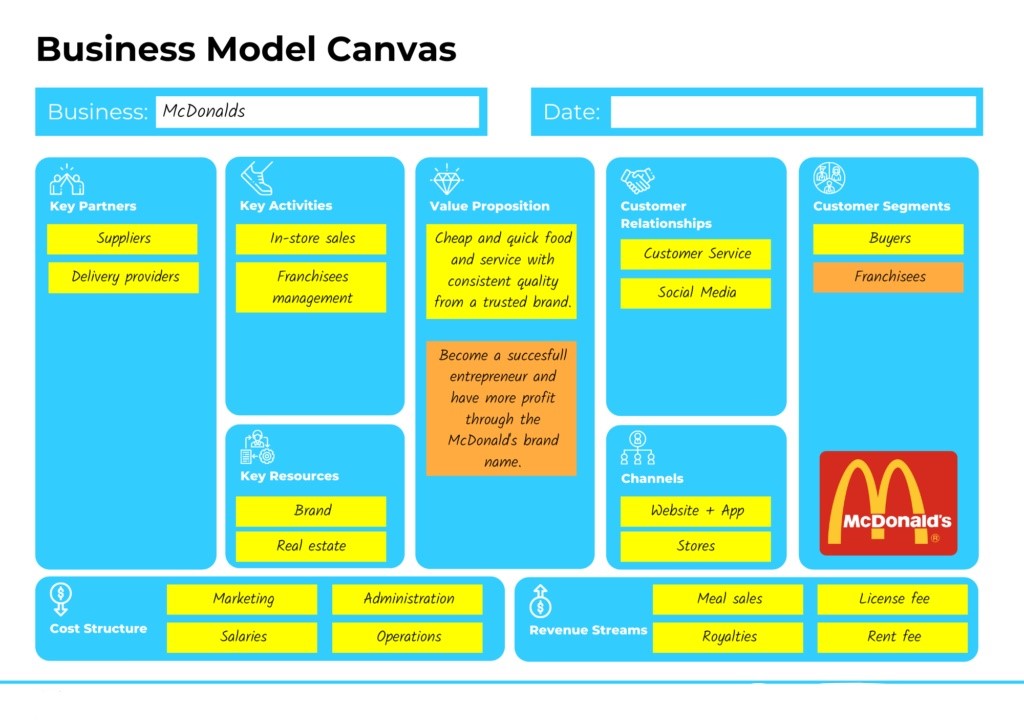
McDonald’s Mission Statement
McDonald’s commercial charge is centered on being the preferred destination for guests to enjoy their refection’s and potables. This charge underscores the significance of guests as the central focus of the business, while also emphasizing McDonald’s part as a significant influencer in their food and libation choices. The main factors of McDonald’s commercial charge statement are
- Being the guests’ favorite place to eat and drink.
- Being the guests’ favorite way to eat and drink.
McDonald’s has remained committed to its mission of “Quality, Service, Cleanliness, and Value,” upholding each of these attributes throughout its operations. Enhancing customer experience is achieved through a focus on five key fundamentals: people, products, place, price, and promotion.
Furthermore, McDonald’s aims to offer high-quality food at prices that are accessible to people worldwide. The company’s sales are facilitated through an efficient sales channel, ensuring consistently high levels of customer satisfaction at all times.
McDonald’s Vision Statement
McDonald’s Vision Statement can be summarized as striving to accelerate growth and enhance its position as a leading global provider of delicious food, catering to a larger customer base every day. This articulation underscores the company’s commitment to maintaining excellence in food quality while investing in its employees, technology, and resources to foster further expansion. Achieving profitable growth and enhancing customer satisfaction aligns closely with McDonald’s core mission.
The vision statement underscores the pursuit of continuous improvement, as indicated by the aspiration to be “even better.” This reflects McDonald’s ongoing efforts to enhance its service and product offerings, aiming to deliver an exceptional customer experience. By continuously striving for improvement, McDonald’s remains competitive in the dynamic restaurant industry, staying ahead of evolving trends and meeting customer expectations effectively.
McDonald’s Core Values
McDonald’s core values revolve around excellence in quality, service, inclusivity, and value. The company is deeply committed to upholding ethical standards and corporate responsibility as integral components of its identity. This commitment extends to various initiatives, including supporting local communities, ensuring a secure and inclusive work environment, promoting environmental sustainability through responsible practices, offering an affordable menu while upholding food safety standards, and conducting all interactions with unwavering integrity.
McDonald’s Growth Strategy
McDonald’s Corporation introduces a new growth strategy, “Accelerating the Arches,” which encompasses all aspects of McDonald’s business as the leading global omni-channel restaurant brand. This strategy includes a refreshed purpose to nourish and support the communities served by McDonald’s and its franchisees worldwide, updated values to guide actions and behaviors, and growth pillars that leverage McDonald’s competitive advantages.
The growth pillars, rooted in the Company’s identity, MCD, build upon historical strengths and identify areas for further development. Specifically, the Company will activate the MCD in the following ways:
- Maximize Marketing: By investing in innovative and culturally relevant approaches to effectively communicate the brand, food offerings, and purpose.
- Commit to the Core: By responding to customer demand for familiar favorites and prioritizing the delivery of delicious burgers, chicken items, and coffee.
- Double Down on the 3 D’s (Digital, Delivery, and Drive Thru): By capitalizing on competitive strengths and developing a robust digital experience engine that enhances convenience and speed for customers through digital, delivery, and drive-thru channels
In different terms, McDonald’s growth strategy relies on retaining existing customers, winning back those who have drifted away, and enticing occasional customers to become regulars. Moreover, the company has also implemented three key drivers: digital innovation, food delivery services, and enhancing customer experiences. By leveraging technology and human efforts, McDonald’s continuously evolves its interactions with customers, aiming to elevate satisfaction levels and enhance overall experience.

SWOT Analysis OF McDonald’s
McDonald’s Strengths
Leading Brand Status
McDonald’s stands as the 11th most valuable brand globally, boasting a remarkable brand worth of $50.999 billion, firmly establishing its dominance in the restaurant sector amidst intense competition.
Delectable Cuisine
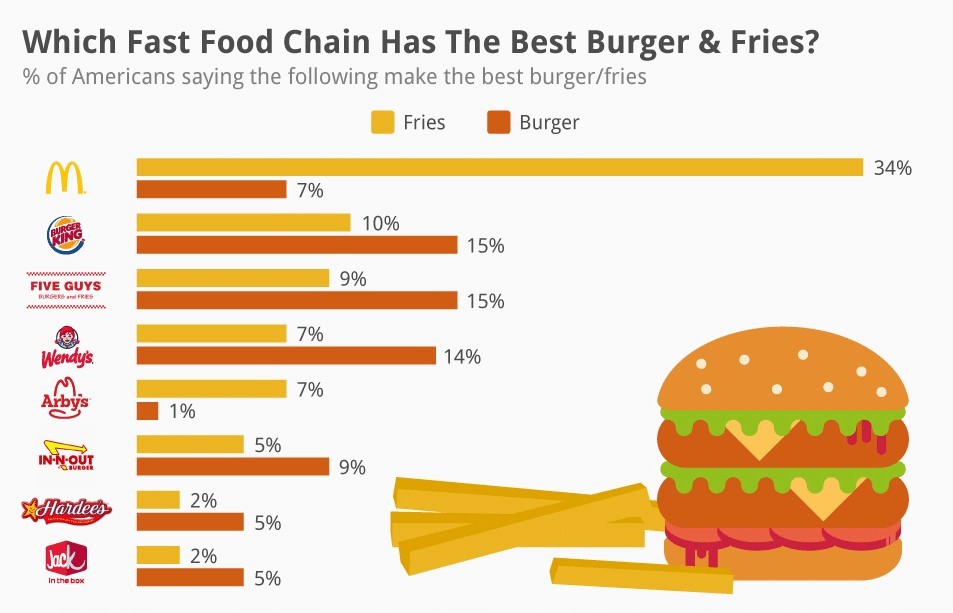
McDonald’s fries are widely acclaimed as the epitome of deliciousness in the fast food realm, reigning supreme according to customer surveys on taste and quality.
Top Ranking in Fast Food Brand Value
McDonald’s proudly holds the title of the most valuable fast food brand worldwide. According to Interbrand’s 2023 report, McDonald’s brand worth surged to $50.1 billion, leaving its competitors far behind. The closest rival, Starbucks, trails with a brand value of $14 billion.
Enhanced Quality Assurance and Health Standards
While opinions may vary on taste and overall dining experience, McDonald’s has consistently excelled in maintaining stringent quality standards. The company rigorously implements comprehensive food safety and quality protocols, ensuring the integrity of ingredients sourced from third-party suppliers.
Moreover, McDonald’s has taken proactive measures to limit the use of high-value antibiotics in its global chicken supply since 2018, aligning with the World Health Organization’s categorization of “highest priority critically important antimicrobials” (HPCIA) for human medicine. This initiative has garnered appreciation from various public health and consumer groups, applauding McDonald’s efforts to mitigate the risks posed by dangerous superbugs.
Discount for Frontline Workers
McDonald’s has extended its gesture of appreciation to National Health Services (NHS) workers by maintaining a 20% discount throughout the entirety of 2022 across all locations in the UK. This discount applies to the entire online menu, allowing frontline workers to enjoy their favorite items while saving money. The initiative was introduced as a way to recognize the hard work of NHS workers during the challenging times of the pandemic.
Center of Excellence on a Global Scale
Hamburger University, McDonald’s flagship training facility, transcends the conventional notion of a school; it embodies an immersive journey. Here, employees cultivate top-tier skills, setting unparalleled standards in value, quality, service, and cleanliness worldwide.
The success of McDonald’s is intricately tied to Hamburger University, renowned internationally for its impact. It goes beyond mere instruction, fostering dedicated teams and instilling an unwavering commitment to excellence. This commitment resonates in every flavor and every service, spanning across the globe.
Technological Innovations
McDonald’s is spearheading innovative technological advancements aligned with its ‘Experience of the Future’ vision. Utilizing artificial intelligence, dynamic menu boards dynamically adjust offerings in real-time based on variables such as weather conditions, time of day, popular orders, and restaurant foot traffic.
The integration of self-service kiosks, mobile ordering platforms, and advanced payment systems further solidifies McDonald’s position as the epitome of the ‘restaurant of the future’.
Innovative Technological Ventures
McDonald’s is embarking on groundbreaking technology ventures to realize its vision of the ‘Experience of the Future’. By introducing innovations such as self-service kiosks, mobile ordering, and payment systems, McDonald’s is enhancing its reputation as the quintessential ‘restaurant of the future’.
McDonald’s Weaknesses
The Franchise Business Structure
McDonald’s serves as a prime example of the international franchising model. However, this intricate network of franchised and company-operated restaurants exposes the brand to various risks.
These risks include financial instability, operational mismanagement, customer dissatisfaction, and diminished revenue generation. The company heavily relies on its franchisees, who operate independently, thus lacking direct control over their day-to-day performance, yet their actions directly impact the brand.
Supply Chain Challenges
As one of the busiest food chains globally, McDonald’s frequently encounters disruptions in its supply chain, leading to issues such as product shortages critical for its operations.
Employee Dissatisfaction
Amidst global movements advocating for enhanced employee rights and increased wage standards, numerous organizations have grappled with significant discontent among their workforce.
McDonald’s, in particular, has encountered considerable backlash from its employees in recent times. Workers have staged protests and strikes, urging the company to raise their minimum wage to $15 per hour. These actions have not only affected McDonald’s reputation but also highlighted the challenges faced by the company in addressing employee concerns.
Sexual Harassment
Sexual harassment means making someone feel uncomfortable or unsafe at work because of their gender. In April 2020, more than 100 female employees sued McDonald’s, saying they were treated badly and harassed while working there. This makes people lose trust in McDonald’s and makes its reputation worse.
Negative Publicity
In June 2020, McDonald’s was accused of firing an employee who had sued them for not keeping employees safe during the recent health crisis. Firing someone for standing up for their rights is wrong and might make other employees scared to do the same.
McDonald’s Opportunities
Value Meals
In 2018, McDonald’s introduced its “$1, $2, $3” menu and the “2 for $5 Mix and Match deal” aimed at customers who want good food at low prices. These menus were very popular and helped McDonald’s sell more food.
Innovative Products
To stay competitive with new fast food places, McDonald’s needs to keep coming up with new and exciting things for people to eat. In 2018, they started selling a special drink called MIX by Sprite Tropic Berry in New York. People loved it so much that they might start selling it all across the US.
Increasing Drive-Thru, Pick-Up, and Self-Order Kiosks
McDonald’s focus on enhancing its dine-in experience proved to be a drawback during the recent health crisis. This approach led to a 17% decrease in earnings as more customers preferred pick-up and delivery options for enjoying their meals at home. To adapt to this shift in consumer behavior, McDonald’s can expand its delivery services, curbside pick-up options, self-order kiosks, and drive-thru facilities to attract more customers during these challenging times.
Mobile Ordering and Delivery
McDonald’s has teamed up with UberEats and DoorDash to provide food delivery services in the US. These mobile order and delivery initiatives enable McDonald’s to adapt to the evolving needs of its customers.
By partnering with DoorDash and Uber Eats, McDonald’s offers meal delivery services in the US, responding to changes in customer preferences. Thanks to these efforts, customers can easily place orders via their smartphones and enjoy the convenience of McDelivery.
This strategic collaboration enhances accessibility and customer satisfaction by expanding McDonald’s presence in the competitive meal delivery market while meeting the evolving expectations of its customer base.
Offering Healthier Choices
As more consumers prioritize healthier eating options, McDonald’s can respond by expanding its range of healthier menu options. While McDonald’s currently offers some healthy choices such as salads and 1% Low Fat Milk Jug, the selection is limited. By increasing the variety of nutritious options, McDonald’s can attract health-conscious consumers and drive growth.
McDonald’s Threats
Intense Competition
While Burger King might seem like McDonald’s main rival, the landscape of competition is evolving.
Recent findings from Restaurant Business indicate that Chick-fil-A has emerged as McDonald’s primary competitor in the fiercely competitive Quick Serve Restaurant (QSR) sector.
Cultural Challenges Across Global Operations
As a global fast-food chain, McDonald’s frequently encounters various cultural challenges in different regions, posing risks to the brand’s image.
Adapting and operating in diverse cultural contexts can be difficult. For instance, McDonald’s faced a significant scandal a few years ago for using non-halal ingredients in Muslim-majority countries. This incident underscores the complexities of maintaining cultural sensitivity and compliance across its international franchises.
Emerging Fast Food Trends
McDonald’s is sometimes viewed by millennials as outdated due to its traditional menu and flavors. In contrast, food chains like Shake Shack and Wendy’s capitalize on this by offering a wide variety of experimental menu items and recipes.
For instance, McDonald’s struggled to keep up with Wendy’s “Signature-Crafted Burgers,” forcing them to rely on their classic Quarter Pounders to maintain their reputation.
Financial Instability
In 2022, McDonald’s experienced a decline in profits for the entire year due to economic instability. This resulted in an 18% decrease in its net income, with the potential for further declines if economic uncertainties persist.
Increasing Health Awareness
As more consumers prioritize healthy living, there is a growing trend towards healthier alternatives such as salads and organic beverages. However, McDonald’s menu predominantly features unhealthy options, risking the loss of health-conscious customers to competitors offering healthier choices.
Stringent Regulations
The surge in lifestyle-related illnesses has prompted many countries to take action. Some nations have implemented regulations to restrict the use of certain unhealthy ingredients or have outright banned fast-food companies. Nine countries, including Iceland, Macedonia, Montenegro, Bermuda, and Bolivia, have enacted bans on McDonald’s operations.

McDonaldization
McDonald’s stands out as a prime example of a globally interconnected organization. The expansion of McDonald’s worldwide is often described as “McDonaldization.” Its success in over 120 countries is attributed to its organizational structure.
The organizational structure of McDonald’s emphasizes localization, ensuring that the entire business model is tailored to appeal to the masses in different countries.
McDonald’s – Future Outlook
McDonald’s has set ambitious goals for its future, aiming to source all customer packaging from renewable, recycled, or certified sources by 2025. Additionally, the company plans to recycle customer packaging in all of its restaurants and address infrastructure challenges to achieve these objectives.
Pioneering Environmental Initiatives
McDonald’s has taken significant steps toward environmental sustainability, becoming the first restaurant company globally to establish an approved Science-Based Target to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It has also joined the “We Are Still In Leader’s Circle,” contributing to efforts to combat climate change.
Commitment to Sustainable Practices
In the USA, McDonald’s has achieved a milestone by serving MSC-certified fish in all of its locations for five consecutive years. Moreover, it has collaborated with Closed Loop Partners to develop a global solution for recyclable and compostable cups through the NextGen Cup Challenge and Consortium.
Leadership in Climate Action
McDonald’s has actively participated in global climate action initiatives, including the Global Climate Action Summit (GCAS), where executive leaders advocated for climate action and presented solutions. Additionally, the company co-hosted the “Path to Greenbuild” event, showcasing its new global headquarters, which has received USGBC LEED Platinum certification.
Setting Industry Standards
McDonald’s is setting a precedent for other fast-food companies to follow. As consumers increasingly prioritize supporting businesses that contribute positively to the world, McDonald’s leadership in sustainability is likely to inspire others in the industry to follow suit.
Conclusion
McDonald’s holds a prominent position as one of the most influential food brands globally, fueled by its extensive globalization efforts and strong customer loyalty. However, despite its enduring legacy, the company must remain vigilant of potential challenges.
Thank you for your interest and for reading!