Tesla Case Study
Introduction:
In the world of cars and energy, Tesla, Inc. shines as a symbol of progress, caring for the environment, and bold entrepreneurship. Started in 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, Tesla has grown into a major player worldwide, thanks to the visionary Elon Musk. Their goal is to speed up the switch to clean energy globally, which has led them to develop innovative electric cars and renewable energy solutions tirelessly.
Early Years and Foundation:
Tesla embarked on its journey with a bold vision to revolutionise the automotive sector through the production of electric cars. Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, inspired by the promise of electric power, established the company in San Carlos, California. Elon Musk, a forward-thinking entrepreneur passionate about sustainable technology, came on board as an investor and chairman of the board in 2004.
Initially, Tesla aimed to develop a high-performance electric sports car that would challenge traditional perceptions of electric vehicles. In 2008, the company reached a significant milestone with the introduction of the Tesla Roadster. This sleek sports car, built on the Lotus Elise chassis and powered by an all-electric drivetrain, showcased not only the viability of electric propulsion but also shattered the misconception that electric cars were confined to dull designs and limited ranges.
Market and Product Range
Tesla stands out as a company dedicated to creating a sustainable future, challenging the dominance of gasoline-powered vehicles with its electric technology. Despite being a relatively small player compared to industry giants like Toyota, General Motors, and Daimler AG, Tesla holds promise for the future, even as it grapples with the scale advantages enjoyed by its competitors. Its market presence spans North America, Europe, and Asia.
In 2008, Tesla introduced its debut vehicle, the all-electric “Roadster,” boasting an impressive range of 245 miles on a single charge. Priced around $109,000, it appealed to affluent consumers seeking eco-friendly sports cars powered by lithium-ion batteries with zero emissions. Transitioning to 2012, Tesla shifted focus to the production of the “Model S,” renowned for its performance, design, and efficiency, targeting luxury car enthusiasts and disrupting the conventional automotive landscape. By March 2014, the Model S claimed the title of Norway’s best-selling car, followed by dominating the all-electric car market in the US by 2017.
Expanding its lineup, Tesla introduced the “Model X” in 2015, a crossover vehicle boasting a battery range exceeding 295 miles, catering to consumers seeking versatility and sustainability. Finally, in 2017, Tesla launched the “Model 3,” designed for mass-market appeal with a price tag starting at $35,000, aiming to make electric vehicles accessible to a wider audience. The diverse range of Tesla models and their impact on the automotive industry are detailed in Annexure: 1(b).
Financial Challenges and the Road to Success
Even though Tesla experienced some initial triumphs, it encountered financial difficulties during its early stages. Elon Musk, understanding the significance of Tesla’s potential in advancing sustainable energy, injected personal finances and pursued external funding to sustain the company. The 2008 financial downturn compounded Tesla’s challenges, but the company successfully obtained a vital loan from the Department of Energy, which proved essential for its survival.
Tesla is forcing the auto industry to change rapidly
While Tesla didn’t invent the electric car (credit goes to Scottish inventor Robert Anderson in 1832), it’s Tesla that brought it into the mainstream since its establishment in 2003. Prior to Tesla’s entry, major automotive manufacturers weren’t focusing on electric cars. However, Tesla changed the game in 2008 with the introduction of the Tesla Roadster, the first luxury electric car, which made electric vehicles appealing.
Following Tesla’s lead, established automakers with ample resources and established supply chains quickly jumped into the electric car market as consumer and government demand for eco-friendly, low-emission transportation grew. Mitsubishi Motors released the next electric car in 2010.
Data from the Bureau of Transportation Statistics indicates that sales of hybrid EVs in the U.S. didn’t surpass 100,000 until 2005. The bureau started tracking EV sales in 2011, which stood at 9,750. Since then, the EV market has seen explosive growth. By 2015, 71,044 EVs were sold in the U.S., along with 384,404 hybrid EVs. Between January and September 2017, Tesla led in EV sales with 73,227 units sold, followed by Chinese automaker BYD with 69,094 units.
According to Brian Loh from McKinsey&Company, the auto industry is experiencing an unprecedented level of innovation. Historically slow to evolve, the industry has been propelled forward largely due to Tesla’s disruptive influence. Tesla’s vehicles have a “cool factor” that traditional automakers lack, generating hype that other brands struggle to match.
Tesla’s Autopilot technology, which enables semi-autonomous driving, has stirred controversy. While some consumers misuse the technology, other automakers are following Tesla’s lead in developing autonomous vehicles (AVs). This has sparked debates in Washington as policymakers balance safety concerns with the industry’s drive for innovation.
Despite its innovative prowess, Tesla also exemplifies the challenges of success in the auto industry, highlighting the importance of stable supply chains.

The Turning Point: Model S and Gigafactories:
The pivotal moment for Tesla arrived with the introduction of the Model S sedan in 2012. With its state-of-the-art technology, sleek aesthetics, and impressive range, the Model S signalled a significant shift in the automotive landscape. Its success positioned Tesla as a major contender in the luxury car market, demonstrating the potential of electric vehicles to outshine traditional gasoline-powered cars.
Concurrently, Tesla pursued another crucial aspect of its mission: sustainable energy production and storage. The company embarked on an ambitious project to construct Gigafactories, large-scale manufacturing facilities dedicated to producing batteries, electric drivetrains, and energy storage solutions. These strategically located Gigafactories not only reduced manufacturing expenses but also played a vital role in expanding Tesla’s production capacity.
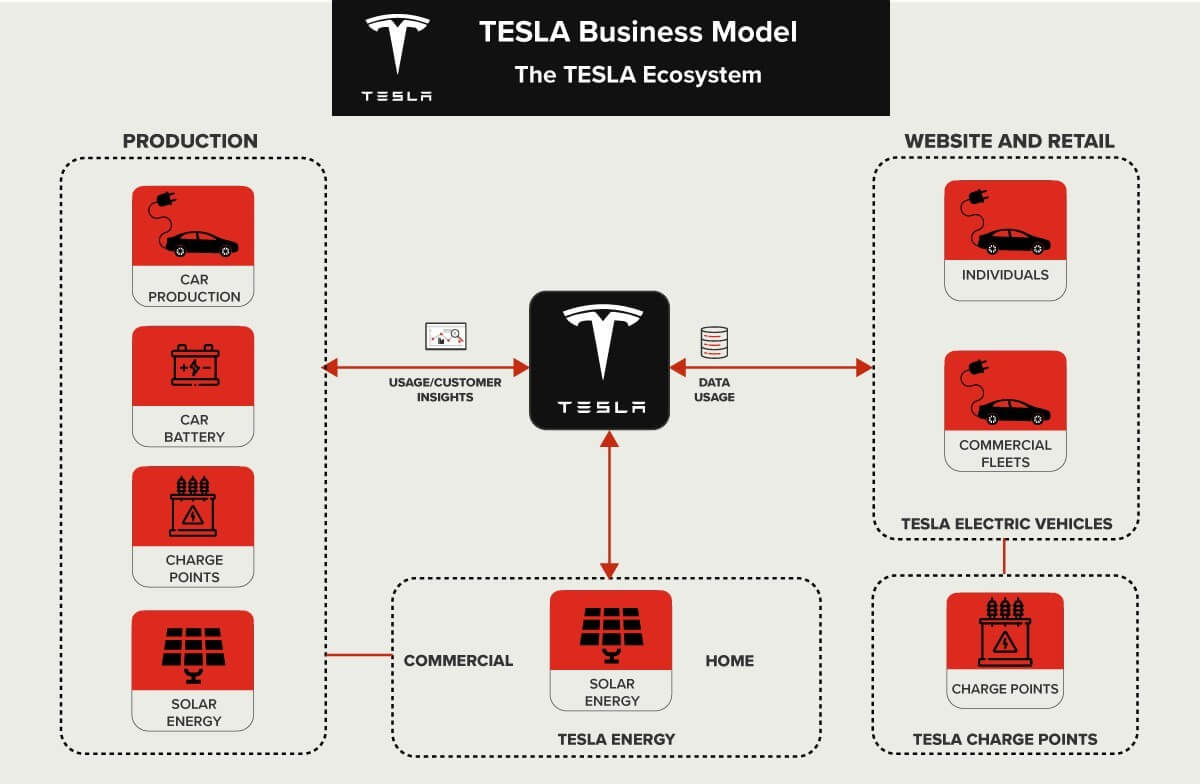
Business Model of Tesla
The Business Model Canvas, developed by Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, provides a comprehensive framework for understanding how a company operates across various dimensions such as key partners, key activities, and value proposition, as depicted in Annexure: 1(a). Tesla’s business model deviates from the conventional approach by vertically integrating processes throughout the value chain, from sourcing materials to final delivery, notably excluding dealerships from vehicle sales.
In addition to manufacturing electric cars, Tesla has diversified into scalable clean energy generation and storage products, as outlined in their corporate profile. The Tesla Gigafactory, operational since 2016 in Nevada, USA, is a prime example. This facility focuses on large-scale production of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles, with the aim of achieving cost efficiencies through in-house manufacturing while also stimulating local economic growth by creating job opportunities.
Tesla’s strategic focus on building an ecosystem centred around sustainable energy is evident. By vertically integrating processes, Tesla aims to reduce its dependence on external suppliers while furthering its commitment to sustainable energy solutions.
Tesla Supply Chain Strategy
Tesla places significant emphasis on automation, procurement, and logistics as key components of its supply chain strategy. Automation plays a central role in Tesla’s approach, aimed at enhancing efficiency and cost reduction throughout the supply chain. By leveraging automated processes, Tesla can streamline operations and minimise expenses. Moreover, automated parts manufacturing ensures that each component meets the company’s stringent quality standards, contributing to overall product excellence.
Tesla’s supply chain strategy encompasses procurement and logistics as integral components. Procurement is a vital aspect, involving close collaboration with suppliers to secure quality parts at competitive prices. Tesla sources components globally, maintaining rigorous quality standards for each part.
Logistics is equally crucial, with Tesla operating its own delivery service to expedite the transportation of parts and finished products efficiently and safely. Additionally, the company partners with third-party delivery services to ensure swift and cost-effective delivery to customers.
Tesla’s success is significantly attributed to its innovative supply chain management approach. Leveraging automation, procurement, and logistics, Tesla efficiently delivers parts and products to customers, contributing to its position as the world’s most valuable automaker.
The Importance of Environmental Sustainability in Tesla’s Supply Chain Strategy
Tesla places a strong emphasis on fostering a healthy and sustainable environment within its supply chain strategy. The company is dedicated to mitigating the environmental impact of its operations, spanning production processes and supply chain activities. To achieve this, Tesla has implemented a comprehensive Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) program, focusing on responsible sourcing, waste reduction, and the promotion of renewable energy sources.
Tesla has taken proactive measures to minimise its carbon footprint and prioritise sustainable sourcing practices. This includes investing in renewable energy solutions like solar and wind power, as well as integrating recycled and biodegradable materials into its manufacturing processes. Furthermore, Tesla collaborates closely with its suppliers to encourage environmentally responsible practices, such as reducing emissions, waste, and water usage, while also advocating for the sustainable utilisation of natural resources.
Tesla has introduced several measures to minimise its packaging footprint, emphasizing the adoption of recycled and recyclable materials while phasing out single-use plastics. The company actively encourages its suppliers to follow suit by reducing their packaging material usage and transitioning to more sustainable alternatives.
Beyond addressing its own environmental impact and that of its suppliers, Tesla advocates for a sustainable supply chain. Initiatives like the Tesla Energy Plan are designed to curtail fossil fuel consumption and advocate for renewable energy adoption. Moreover, Tesla collaborates with suppliers to endorse responsible sourcing practices, encompassing fair labour standards and ethical material usage.
In essence, Tesla’s dedication to sustainability lies at the core of its supply chain strategy. Through initiatives aimed at minimising its own environmental footprint and that of its suppliers, as well as advocating for the adoption of renewable energy sources and ethical materials, Tesla is actively contributing to the creation of a more sustainable future.
Advantages of Tesla’s Supply Chain Strategy
Tesla’s unique supply chain strategy represents an innovative approach to supply chain management, resulting in notable cost reductions and accelerated time-to-market. Central to this strategy are three key elements: real-time visibility, flexible inventory management, and automation.
Real-Time Visibility
Tesla prioritises real-time visibility across all aspects of its supply chain operations. This allows the company to promptly identify and address potential issues such as component shortages or delivery delays. By swiftly taking corrective actions, Tesla ensures efficient inventory management and timely provision of parts for vehicle production.
Flexible Inventory Management
Tesla capitalises on its ability to swiftly adjust inventory levels, enabling rapid responses to fluctuations in customer demand. This agility ensures that Tesla maintains optimal stock levels, meeting customer requirements amidst short production and delivery cycles.
Automation
Automation plays a pivotal role in Tesla’s supply chain strategy. Leveraging automated systems for inventory management, order processing, and part tracking enhances operational efficiency and reduces labour costs. Moreover, automation provides Tesla with comprehensive visibility into its supply chain activities, facilitating streamlined operations.
By integrating these three elements, Tesla has established a robust and cost-effective supply chain model, enabling significant cost savings and expedited time-to-market, essential for its success in the automotive industry.
Challenges Faced by Tesla’s Supply Chain
Although Tesla’s Unconventional Supply Chain strategy offers numerous benefits, the company still encounters several challenges that need to be addressed:
Quality Control
Tesla heavily relies on automated systems for inventory management and order processing, posing a risk to quality control if these systems are not properly maintained or become outdated. Ensuring the maintenance and modernization of these systems is crucial for upholding product quality.
Logistical Challenges
Tesla’s supply chain heavily depends on efficiently shipping parts from suppliers to its factories. Any disruptions in this complex logistics network can lead to delays in parts delivery, impacting production schedules.
Resource Constraints
As Tesla’s supply chain model is relatively new, the company may face limitations in resources. This can hinder its ability to handle unforeseen changes in customer demand or swiftly adopt new technologies.
Despite these challenges, Tesla has achieved significant cost savings and time-to-market advantages through its supply chain strategy. By investing in its supply chain infrastructure and addressing these challenges, Tesla can maintain its competitive edge in the automotive industry.
Tesla’s Customer Segments
Tesla has diversified its vehicle offerings to cater to a wide range of customers. It offers mid-market vehicles with affordable pricing, as well as high-end luxury and sports cars, competing with brands like Porsche and Ferrari. Furthermore, Tesla has ventured into the commercial vehicle sector, providing environmentally friendly options for transportation and shipping. It’s important to note that Tesla’s customer base includes not only fast and eco-friendly car enthusiasts who appreciate features like autopilot but also followers of Elon Musk, who are drawn to the company’s visionary leadership.
Tesla’s Value Propositions
In the realm of automobiles, Tesla offers a value proposition centred around environmental sustainability coupled with high performance, innovative design, enhanced functionality, efficiency, extended range, flexibility, and cost-effective (or complimentary) recharging options. Beyond its vehicle lineup, Tesla also markets home batteries and solar panels to both residential and commercial clients, offering convenient power solutions. Furthermore, Tesla continues to supply systems and components to other automotive manufacturers, along with providing financial services such as loans and leases.
Tesla’s Customer Relationships
At the core of Tesla’s philosophy lies a strong emphasis on customer relationships, which has been evident since its inception. The company has diligently focused on enhancing the customer experience, exemplified by its decision to adopt a direct-to-customer sales model through company-owned stores instead of traditional dealerships. Moreover, customers have the convenience of browsing, selecting, and customising their vehicles directly through Tesla’s website.
Furthermore, Tesla has been steadily expanding its charging infrastructure to facilitate faster and more affordable charging for Tesla vehicle owners. This investment underscores Tesla’s commitment to providing a seamless and convenient ownership experience.
Tesla has also cultivated a highly favourable brand image and reputation among the public, synonymous with luxury, cutting-edge technology, and innovation, all while prioritising environmental sustainability.
Tesla’s Key Activities
Tesla’s primary activities encompass:
Car Manufacturing: Tesla remains dedicated to delivering on its promise of electric vehicles. This entails investing in the production of not only cars but also batteries and solar energy panels.
Research and Development (R&D): Constant innovation drives Tesla’s quest for advanced and environmentally friendly technology.
Design: Tesla prioritises design as a distinguishing factor for its products. Elon Musk emphasised early on that, given the inherent costliness of its technology, Tesla would invest in design rather than engaging in price competition.
Infrastructure Development and Maintenance: Tesla is actively expanding its network of recharge stations globally, aiming to facilitate wider adoption of electric vehicles.
Software Development: Agile principles guide Tesla in the continual development and improvement of its software systems.
Sales and Marketing: Tesla adopts a customer-centric approach, focusing on delivering exceptional customer experiences rather than traditional advertising methods.
Tesla’s Key Partners
Tesla’s key partnerships and alliances play a crucial role in its operations:
- Suppliers: While Tesla manufactures the majority of its car components in-house, it relies on third-party suppliers for certain parts like windshields and brakes. These suppliers are essential partners enabling Tesla to produce and deliver its vehicles efficiently.
- Alliances: Tesla has formed strategic alliances to strengthen its position in the electric vehicle market. For instance, it collaborated with Toyota to co-develop electric vehicle parts and systems, enhancing its market presence. Additionally, Tesla has partnered with Panasonic in the construction of a manufacturing facility in New York focused on large-scale battery and solar cell production.
- Government: Tesla benefits from tax incentives provided by the U.S. federal government due to its emphasis on eco-friendly vehicle and energy development. These incentives, coupled with the company’s contribution to job creation in the U.S., further support Tesla’s growth initiatives.
- Charging Points: Tesla collaborates with various establishments such as hotels, resorts, restaurants, and shopping centres to establish fast car charging stations. These partnerships enable Tesla to expand its charging network, providing convenient recharging options for its customers.
Tesla’s Cost Structure
Tesla’s cost structure encompasses various components typical of any manufacturing entity, such as:
- Manufacturing expenses, covering the production processes.
- Sales-related costs, including marketing and distribution expenditures.
- Administrative expenses, encompassing overhead costs associated with general operations.
- Research and development (R&D) expenditures, focusing on innovation and product enhancement.
Tesla’s Competitors
Nio: Established in 2014, Chinese automaker Nio specialises in manufacturing high-end electric vehicles for global markets. While experiencing sales growth exceeding 100% annually, the company operates fewer than 200 battery stations in China, indicating significant potential for expansion.
Ford: Venturing into the electric vehicle market, traditional automaker Ford has witnessed sales of electric cars surging by over 70% yearly. Notably, a majority of these customers are new to the Ford brand, leveraging the company’s extensive experience as one of the oldest players in the automotive industry.
Volkswagen: Despite launching its first electric vehicles a decade after Tesla, German giant Volkswagen anticipates that half of its U.S. sales will comprise electric vehicles by 2025, aiming to manufacture 1.5 million units within that time frame. Benefitting from its long standing brand heritage, Volkswagen represents a formidable competitor.
Li Auto: Emerging in 2015, Chinese newcomer Li Auto has impressed with its rapid technological advancements, achieving remarkable growth by selling over 10,000 electric vehicles in its inaugural year in China.
Nikola Corp: Pioneering a hybrid approach, Nikola Corp integrates electric battery and hydrogen fuel cell technologies in its vehicles, primarily focusing on large trucks. Founded in 2014 in the U.S., Nikola maintained zero emissions from 2016 to 2020.
Workhorse Group: U.S.-based Workhorse Group specialises in electric vans tailored for delivery services. Having fulfilled a substantial order of 950 vans for UPS, the company, established in 1998, transitioned into electric vehicles in 2015.
Canoo Holdings: A recent entrant, Canoo Holdings introduces a unique business model set to debut on roads in 2022. Offering a distinctive value proposition, Canoo will offer its vehicles through a subscription-based service, diverging from traditional ownership or leasing models.

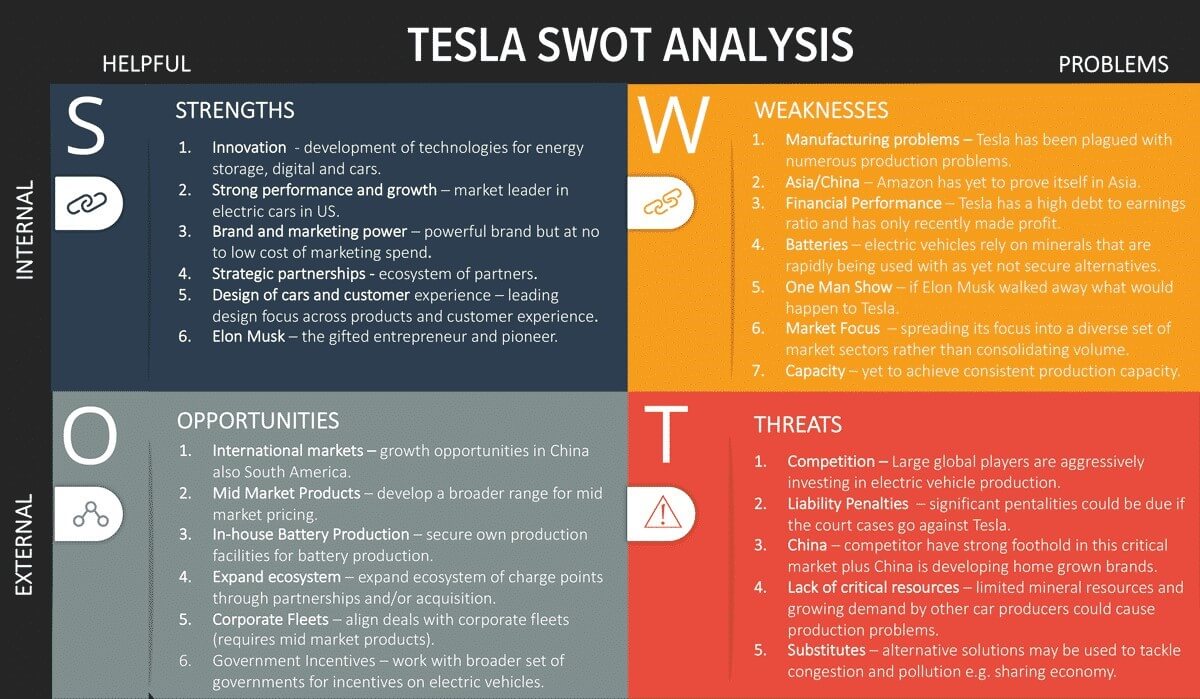
Tesla’s SWOT Analysis
Tesla’s Strengths
Tesla stands out in several key areas:
- Energy Efficiency: Tesla leads the market not only in sales volume but also in its commitment to renewable energy sources such as solar power.
- Partnerships: The company collaborates with major energy firms, expanding its efforts in renewable energy.
- Top Employer: Recognized by Forbes as one of the best employers in 2019, Tesla boasts a diverse corporate culture that appeals to young professionals.
- Leadership: With its exceptional growth and dominance in electric vehicle (EV) sales, Tesla emerged as the most valuable automotive company in 2020.
- Innovation: Tesla’s significant investments in research and development drive the creation of new technologies and ensure superior design and comfort, enhancing its appeal to consumers.
- Brand: Tesla established itself as the foremost electric vehicle manufacturer in a market with limited competition at its inception. The company enjoys a strong reputation for both developing clean energy solutions and delivering profitable products, fostering trust among consumers.
Tesla’s Weaknesses
Tesla faces several challenges:
- Manufacturing Constraints: Tesla operates with a smaller manufacturing footprint compared to traditional automakers, leading to production limitations and distribution delays.
- Limited Global Presence: While experiencing growth, Tesla’s primary market remains the United States, with over 70% of its revenue generated there. Expansion efforts face challenges in establishing a strong presence worldwide.
- Premium Brand Positioning: As a premium brand in the clean energy sector, Tesla targets a niche market segment due to its high-priced products, limiting its customer base.
- Financial Concerns: Tesla’s high operational costs contribute to cash burn, posing a threat to its profitability and investor confidence.
- Dependency on Elon Musk: The prominent role of CEO Elon Musk has become synonymous with Tesla’s brand, raising concerns about succession planning and the company’s long-term stability.
Tesla’s Opportunities
Tesla has opportunities in several key areas:
- Global Expansion: While the United States and China currently drive the majority of Tesla’s sales, there is significant potential for expansion into other markets, particularly in Asia, including China and India.
- Autopilot Technology: Tesla’s autonomous driving technology, known as Autopilot, has garnered widespread attention for its safety and convenience. Continued development and improvement of this technology present opportunities for further market penetration and adoption.
- Sustainability Trend: With increasing awareness and concern about environmental issues, there is a growing demand for sustainable products. Tesla’s focus on sustainability aligns well with this trend, offering opportunities for continued growth in market share.
- Battery Production: Tesla’s efforts to vertically integrate battery production by manufacturing its battery cells in-house offer opportunities to reduce production costs and create new job opportunities while ensuring a consistent and reliable supply of batteries for its vehicles.
Tesla’s Threats
Tesla faces several challenges:
- Competition: Established automotive companies, with centuries of experience, are rapidly investing in electric car technology, potentially offering more affordable products that could challenge Tesla’s market dominance.
- New Technologies: The automotive industry is evolving rapidly with innovative technologies and alternative energy sources, which may increase Tesla’s operational costs and reduce profit margins as it strives to stay at the forefront of innovation.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The lack of adequate regulations for autonomous vehicles poses a risk to Tesla’s future plans, particularly regarding its development of self-driving technology.
- Long-term Sustainability: Clean energy companies require robust long-term sustainability strategies, and Tesla’s limited infrastructure may not be sufficient to support its ambitious goals in the long run.
- Elon Musk’s Image: While Musk is widely regarded as a visionary, his controversial behaviour and erratic public statements have sometimes tarnished Tesla’s reputation and raised concerns among investors and the public alike.
Conclusion
While Tesla didn’t pioneer the electric car, it significantly revitalised the market by introducing vehicles with distinctive designs, durable batteries, and an extensive technological infrastructure for support and maintenance. Moreover, Tesla adopted a unique business model by directly selling to consumers, bypassing traditional middlemen. Consequently, Tesla has emerged as one of the most successful players in the automotive industry today. With Elon Musk and his team at the helm, the company continues to explore innovative transportation methods, solidifying its position as an industry leader.